Dwarfism - Friesian Horse
Description: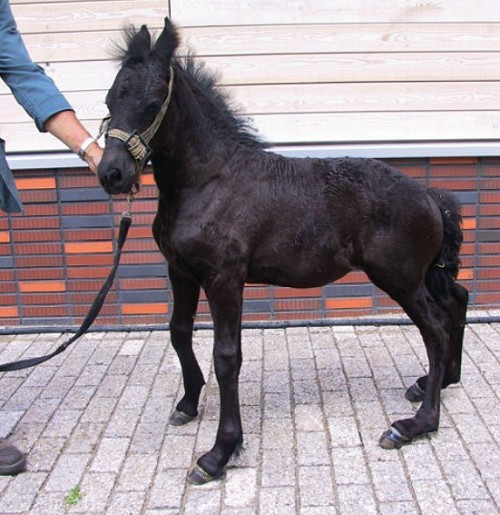
A genetic condition in Friesian horses results in a disproportionate form of dwarfism. This form of dwarfism is characterized by abnormally short limbs while the size of the head and length of back are normal. Affected foals also suffer from flexor tendon laxity, which is characterized by loose ligaments and can be painful. Unlike normal foals that grow out of this as they mature, horses impacted by this form of dwarfism continue to be impacted by the condition often resulting in an abnormal gait.
Researchers in the Netherlands identified a mutation (c.50G>A) in exon 1 of the Beta-1,4-Galactosyltransferase 7 (B4GALT7) associated with this disorder. B4GALT7 plays an important role in proper formation of the extracellular matrix, a key element in bone development. The impact of the mutated gene affects normal collagen and bone development in the affected areas of the body.
Dwarfism in Friesian horses is an autosomal recessive disorder. This means that a horse must inherit two copies of the mutation in order to present symptoms of dwarfism. If two carriers are bred to one another, there is a 25% chance per horse born that they will develop symptoms of dwarfism and a 50% chance per horse born that they will also be carriers of dwarfism. Because dwarfism is not treatable, the best way to manage dwarfism is through prevention. Genetic testing can reveal the likelihood of a horse developing dwarfism and can inform a breeder of major health concerns. Testing shows that roughly 12% of the Friesian horse population carries the mutated gene.
Breeds Affected:
Testing for this form of Dwarfism is valid for Friesian horses and horses with Friesian ancestry.
Additional Tests For Friesian Horses:
Test Results:
Animal Genetics offers DNA testing for a form of Dwarfism found in Friesian horses. The genetic test verifies the presence of the G>A mutation and presents results as one of the following:
| D/D | Affected | The horse carries two copies of the mutation and is homozygous for Dwarfism. The horse is affected. |
| N/D | Carrier | Both the normal and mutant alleles were detected. Horse tested heterozygous for Dwarfism and is a carrier of the mutation associated with your breed. |
| N/N | Clear | Horse tested negative for Dwarfism and does not carry the gene mutation. The horse will not pass on the defective gene to its offspring. |
References:
Leegwater P.A., Vos-Loohuis M., Ducro B.J., Boegheim I.J., van Steenbeek F.G., Nijman I.J., Monroe G.R., Bastiaansen J.W., Dibbits B.W., van de Goor L.H., Hellinga I., Back W. & Schurink A. (2016) Dwarfism with joint laxity in Friesian horses is associated with a splice site mutation in B4GALT7. BMC Genomics 17: 839. doi 10.1186/s12864-016-3186-0.
Submit a Sample for Testing:
To submit a sample for testing please click on ORDER and download a sample submission form. Then follow the sample collection and submission instructions.
Cost per sample is $45.00. Please see our Equine Fee Schedule for all equine testing rates.